Determine the Molarity of a Solution
Molarity refers to the concentration of a given solution. The new molarity can be easily calculated by the solution dilution calculator and solved for M2 using the above equation.

Question Video Calculating The Molarity Of A Solution From Mass And Volume Nagwa
The mixing process of a solution happens at a scale where the effects of chemical polarity are involved resulting in interactions that are specific to solvation.

. M nV where n is the number of moles and V is the volume in litres. Depending on the solution and the scientist Molarity MolesLiter. Molarity of NaOH 02 M Volume of solution 100 mL Molarity of HAc 01 M Ka for HAc question_answer Q.
If you need to calculate diluted molarity you can use the following formula. The pH of any aqueous solution at 25texto is always 14. N M V Example.
The lab allows students to select from hundreds of standard reagents aqueous and manipulate them in a manner resembling a real lab. Molarity is the number of moles of a substance in one litre of solution. What is the pOH of a solution at 25texto.
More information and offline downloads. It is designed to help students link chemical computations with authentic laboratory chemistry. The product of molarity and volume of the sodium hydroxide provides the moles of the solution and the moles are equal in the acetic acid when completely.
Normality is similar to molarity except it expresses the number of active grams of a solute per liter of solution. This color change is termed the endpoint of the titration. An increase in the molarity of a solution causes a considerable decrease in its pH that could be noticed by using a pH calculator from molarity.
Correct The solution is 50 Molar. This example has neither the moles nor liters needed to find molarity so you must find the number of moles of the solute first. Sodium chloride has a valence of 1 and a molecular weight of 58443.
In chemistry a solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. Concentration can be recorded and reported in many different ways depending on the solution the scientist and. For acid solution n is the number of H ions given by a formula unit of acid and for a basic solution n is the number of OH- ions given by a formula unit of a base.
Particles are evenly. M_2 M_1 V_1 V_2 20M 100mL 500mL 156 M HCl Thus the solution is diluted due to the new volume that is five times extra then the original volume. Grams active solute per liter of solution.
But when mixing a chemical solution you can determine the expected pH using well-studied well- documented stoichiometric theory. Incorrect The solution is 50 Molarity. In order to determine when a solution has been exactly neutralized an acid-base indicator is used that changes color in a certain pH range pH is a scale used to measure acidity.
The molarity definition is based on the volume of the solution NOT the volume of water. The official symbol for molarity is c concentration but many people use the old symbol M. There is particle homogeneity ie.
In such a mixture a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance known as a solvent. Molarity M is defined as the number of moles of a solute in a litre of solution. 064 M and 38 lower than claim First you want to start by using the titration information to find the molarity of the acetic acid.
Note that we often use square brackets around the formula of solvated species to indicate the molarity of a solution the concentration of the solution in mol L-1. Using the Ka values in Table 96 calculate the pH of a buffer that contains the given. Dissolve sodium chloride NaCl in water.
The Virtual Lab is an online simulation of a chemistry lab. The valency is generally measured. Please scroll below to find our collection of.
The molarity of the K2SO4 solution 228 M The mass of K2SO4 37 g The molar mass of K2SO4. When dealing with reactions that take place in solutions the related concept of molarity is useful. MolsL M Massvolume gramsL.
Therefore the equivalent weight is 584431 or 58443. Molarity also means the same as molar concentration. Common examples of solutions are sugar in water and salt in water solutions soda water etc.
What is a Solution. What volume of solution mL is required to prepare a 228 M solution with 37 g of K2SO4 MM 1743 A. How to Calculate Normality of a Chemical Solution.
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm. 1 gram of NaCl is dissolved into 005 L of water so the normality of the solution is. Where M concentration in molarity and V volume.
The volume of the solution is essentially calculated in the unit of liters. Because the pH of a. Note our solvent could be distilled and carbon dioxide free water.
Molarity M-is the molar concentration of a solution measured in moles of solute per liter of solution. It is measured by considering two indicators that is the number of moles that are present in the solute and the volume of the solution. By definition its the number of moles of a solute or substance dissolved in a liter of a solution.
Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 237 grams of KMnO 4 into enough water to make 750 mL of solution. There are two individual formulas for both an acid solution and a basic solution. Molarity concentration molar mass.
GL or mgml Normality moles of active ionsL N We talk about solutions in terms of concentrations how much of each substance or solute the solution contains. Find expected pH for a given concentration simply by entering the molarity or enter weight and total. This is the same with molar concentration and represents the concentration of a solute in a solution.
For example an aqueous solution of sodium chloride NaCl aq with a molarity of 0154 mol L -1 or 0154 mol dm -3 could be represented as. The mole can be used to determine the simplest formula of a compound and to calculate the quantities involved in chemical reactions. Unit of measurement.
Molarity mole of soluteliter of solution. What is the molarity. Molarity also known as the molar concentration of a solution is the technique of calculating the amount of substance a particular chemical solution contains.
From basic molarity formula we have obtained mole of solute NaOH is equivalent to. Normality is often used in acid-base reactions or when dealing with acids or bases. The pH calculator tool provides expected pH values for a variety of common laboratory and industrial chemicals.
This is the gram equivalent weight of solute per liter of solution. It is defined as the number of moles in a solution. In a solution all the components appear as a single phase.
M_1V_1M_2V_2 Where 1 is the acetic acid and 2 is the sodium hydroxide. If three of the above quantities are known the fourth can be calculated. An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is waterIt is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending aq to the relevant chemical formulaFor example a solution of table salt or sodium chloride NaCl in water would be represented as Na aq Cl aqThe word aqueous which comes from aqua means pertaining to related to similar to or dissolved in.
We can rearrange this equation to get the number of moles. Add water to make the diluted solution volume 900 ml. Level 1- Given moles and liters.
The normality of a solution is never less than its molarity. MolL The concentration may also be expressed in different fractions of the molar concentration such as mmolL mM μmolL μM nmolL nM.
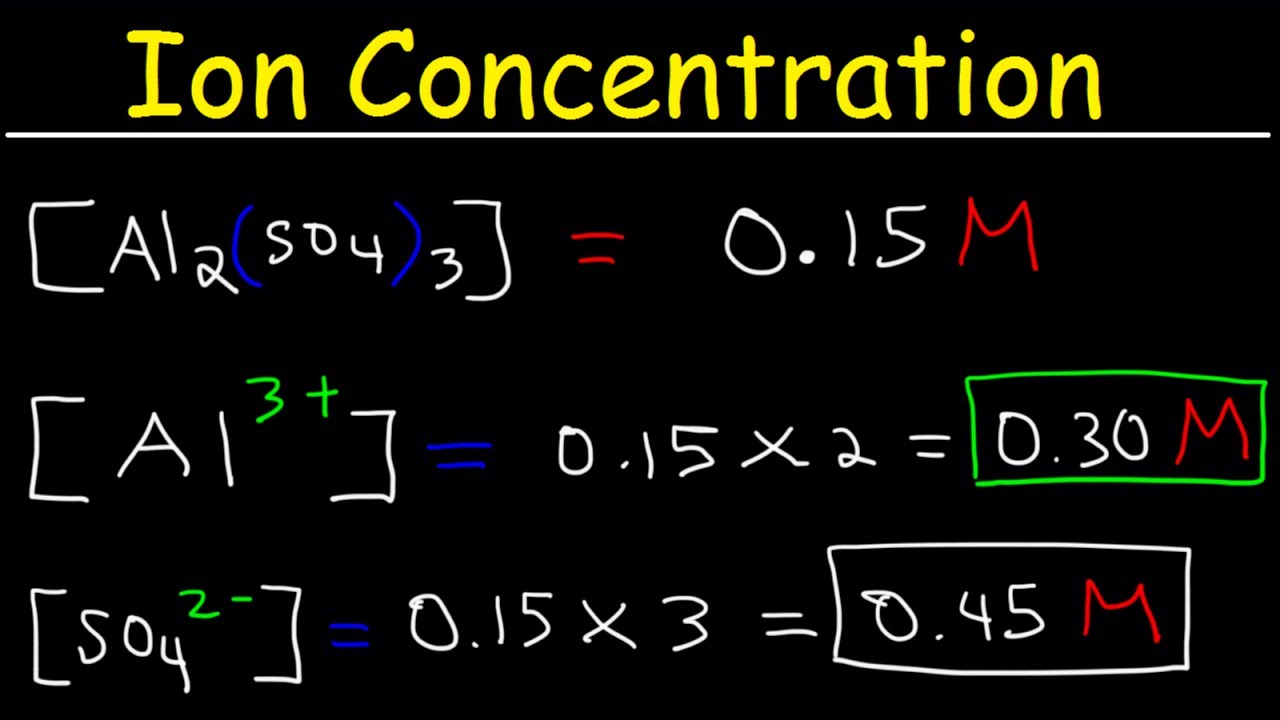
Molarity Practice Problems Youtube

6 1 Calculating Molarity Problems Chemistry Libretexts

How To Calculate Molarity Using Solute Mass Chemistry Study Com

Molarity Chemistry Tutorial Youtube

What Is The Molarity Of A Solution That Contains 2 17 Moles Of Srcl 2 In 2 660 Ml Of Solution Homework Study Com

Molarity Chemistry Tutorial Youtube
0 Response to "Determine the Molarity of a Solution"
Post a Comment